The Global Business Complexity Index (GBCI) 2024 provides an authoritative overview of the complexity of establishing and operating businesses around the world. It explores factors driving the success or failure of international business with a focus on operating in foreign markets, and outlines key themes emerging globally as well as local intricacies across 79 jurisdictions.
The research for the report explores 292 different indicators relating to business complexity, to provide in-depth insight into the global and local challenges that impact the ease of doing business across the world.
This year's analysis has revealed three global trends that impact upon business complexity:
- Investing safely and securely in high complexity jurisdictions
- Multinational risk and how it shapes the business environment
- Growth in uncertain times – strategies for success
We explore the third theme in this article, examining how organisations are adapting staffing levels to navigate the uncertainty of the business environment. This includes an assessment of how they attract and retain staff, while also exploring the benefits of working with a local workforce.
Most jurisdictions are finding the retention and attraction of talent a difficult challenge to overcome, with factors preventing an agile workforce tending to relate to specific regulatory or economic environments. Compliance with ESG legislation also continues to be a struggle for certain regions, with opinion divided on their jurisdiction's ability to prepare for new or unexpected ESG requirements.
Growth opportunities can be found in regional competition and workforce availability
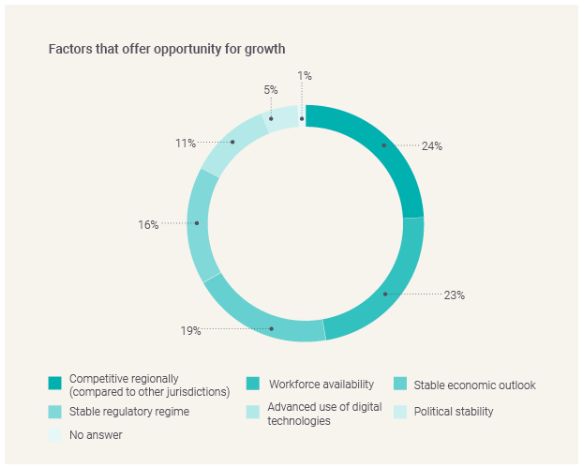
Jurisdictions identified being more competitive than their neighbours as a major driver of growth. This is closely followed by workforce availability. Being competitive regionally allows jurisdictions to stand out within an area and become the most attractive option for foreign investors. This can be for a variety of reasons, including ease of setting up a business, reduced complexity around regulatory compliance, transparent regulations and even natural resources.
Interestingly, this is slightly different when split by complexity — where the top 10 most complex jurisdictions find growth in the competition their jurisdiction offers, in comparison to other regions, while the bottom 10 find growth in stability. Similarly, whilst South American jurisdictions benefit from regional competition, APAC and North America benefit from their respective stable economic outlooks and regulatory regimes.
Areas that drive growth are diverse, with the contribution of technology most common
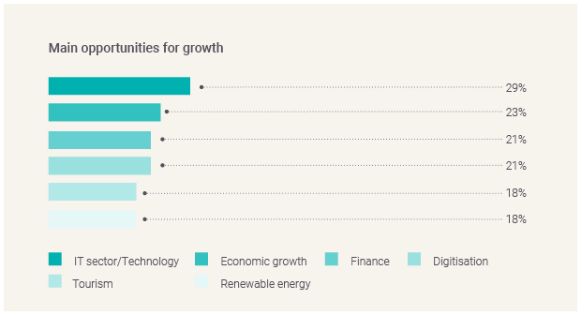
Although jurisdictions named a variety of factors that impact growth, IT and technology topped the rankings as most influential. Jurisdictions in North America showed a slight deviation, with tourism placing particularly high at 33%.
Technology offers growth in multiple ways. It can provide growth opportunities where countries possess technological manufacturing expertise and can increase their market share through production. Using technology to boost productivity was also identified in relation to workforce streamlining. Multiple jurisdictions, including New Zealand and Hong Kong, SAR, were seeing companies automating back-office, entry level and part-time jobs using generative AI to keep workforce numbers low and focus on higher value tasks.
Opinion is split on businesses' ability to quickly adapt staffing levels to meet demand
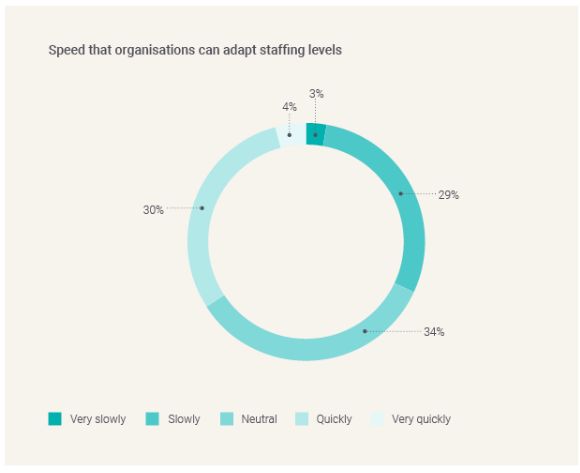
One third of jurisdictions feel they can adapt staffing levels quickly to meet demand (34%), while a similar proportion suggest a slower pace (32%). When split by regions, South America and APAC are more able to adapt staffing levels quickly (at 50% for both), while nearly half of EMEA jurisdictions (46%) report only being able to adapt slowly.
The ability to effectively respond to demand is largely dependent on two dynamics: local labour laws and regional talent. Jurisdictions with tight labour laws and a strong union presence – or those with a shortage of available talent – are much less able to adapt staffing levels responsively.
TMF Belgium expert
The majority of jurisdictions find it challenging to retain and attract talent
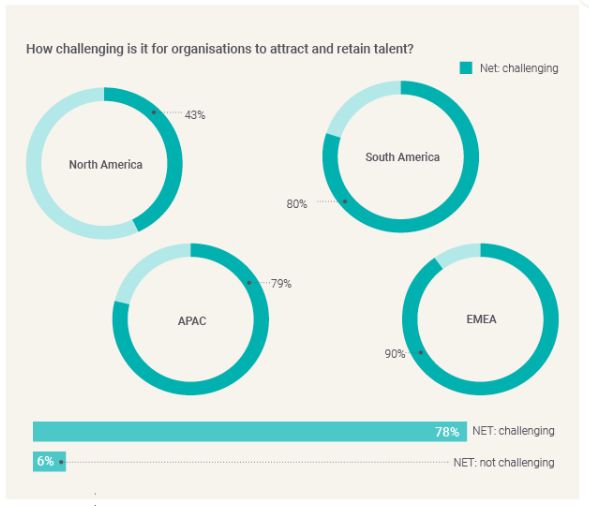
A large majority of jurisdictions find it challenging to attract and retain talent (78%) – with this number even higher for the EMEA (90%) and APAC (79%) regions. In contrast, only 43% of North American organisations find it challenging to attract talent. The North American results may be linked to the limited, albeit improving, severance packages operable in the US, where greater turnover of staff will have a limited impact on businesses' bottom line.
Factors preventing an agile workforce tend to relate to the regulatory or economic environment of a jurisdiction
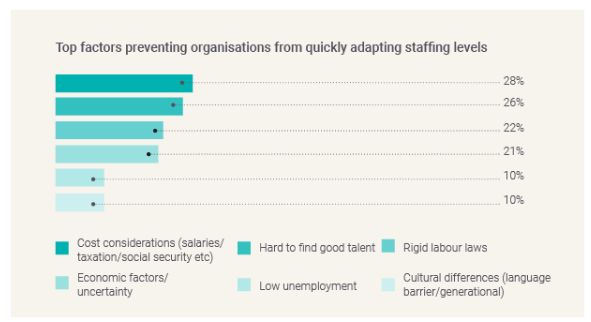
High costs, elusive talent, rigid labour laws and economic uncertainty were all cited as key factors preventing organisations from quickly adapting staffing levels.
High costs were more strongly emphasised in South America at 38%, compared to 28% overall. Meanwhile, jurisdictions in EMEA find it particularly difficult to find good talent at 36%, compared to 26% overall. High costs tended to be linked to a limited talent pool, where trained talent had either moved elsewhere or were demanding higher salaries due to an increased cost of living.
TMF Switzerland expert
In some jurisdictions, union presence can make it costly for businesses to invest in the local workforce, with tight laws on severance and pay packets.
TMF Argentina expert
Despite the barriers in hiring staff, TMF Group experts highlight several areas of opportunity in attracting and retaining talent
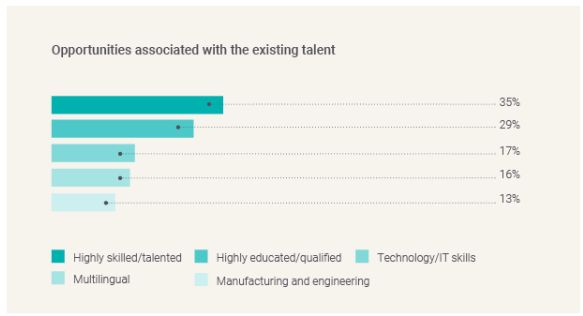
Many TMF Group experts cited the availability of a highly skilled and educated workforce – specifically expertise in IT, engineering, finance and technology – as a crucial benefit of existing talent in certain jurisdictions. Several experts also emphasised the multilingual skills of the local workforce as a great opportunity for investment, particularly in the increasingly global context of business operations.
In the majority of jurisdictions, companies are required to abide by at least one ESG legislation
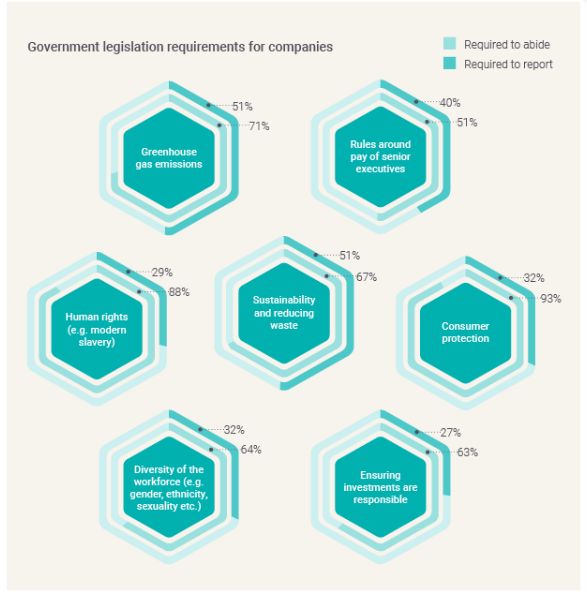
Consumer protection and human rights are embedded regulations, with large proportions of jurisdictions having to abide and report by these legislations. In only two jurisdictions, namely Curaçao and Venezuela, are companies not required to abide by any ESG legislation and/or report on their activities. Higher proportions have to abide by human rights legislation in EMEA (95%) and North America (93%), compared to 88% overall.
Legislation on greenhouse gas emissions, sustainability and reducing waste also feature highly, with over half of all jurisdictions needing to report on their activities. This continues an upward trend on reporting on environmental sustainability from 2023, with many governments and authorities making a concerted effort to hold businesses to account in reducing their carbon footprint.
This is a slightly different story in South America, with a large proportion of South American jurisdictions not required to abide by or report on sustainability legislation (40%) or human rights (40%). TMF Group experts noted how political instability in the region, namely in Argentina, Peru and Bolivia, can make it difficult for ESG legislation to be sustained or prioritised.
There is a split among jurisdictions feeling prepared for new or unexpected ESG legislation
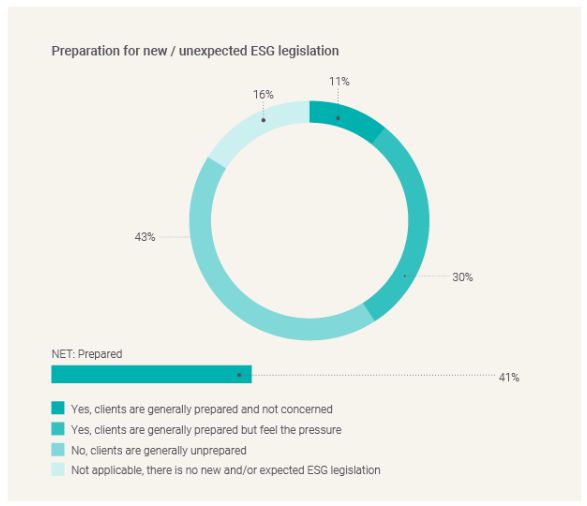
While 41% expressed preparedness, a third of jurisdictions still feel the pressure around ESG legislation. Adhering to global sustainability standards (28%) and cross-industry ESG reporting (26%) are the two most common elements of changing ESG legislation that can create complexity for jurisdictions. This is particularly the case in APAC jurisdictions, scoring 46% and 62%, respectively.
Given reporting requirements for ESG are likely to increase, it is likely that companies will continue to feel this pressure. It is expected that the level of reporting will only become more pronounced – moving away from box-ticking exercises and toward more in-depth metrics.
The Global Business Complexity Index 2024
This article is an extract from TMF Group's latest report, the Global Business Complexity Index 2024.
Explore the GBCI rankings, analysis and global trends, to help you cut through the layers of corporate compliance complexity – download the full report here.
To find out more about the drivers of business complexity in the jurisdictions that matter to you, explore our Complexity Insights Dashboard.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.


