Legislative changes (To be effective from the date of enactment of the Finance (No. 2) Bill 2024)
Amendments under Customs Act:
[Clause 100]
- Section 28 DA is being amended to accept different types of proof of origin to align with new trade agreements, allowing for self-certification.
[Clause 101]
- A proviso is being inserted to Section 65(1) to empower the Central Government to specify certain operations related to a class of goods that shall not be permitted in a warehouse.
[Clause 102,103]
- Section 143AA is being amended to facilitate trade by replacing the expression "a class of importers or exporters" with "a class of importers or exporters or any other persons". The same change is being made to Section 157(2)(m).
Amendments under Customs Tariff Act:
[Clause 106]
- Section 6, which provided for the levy of protective duties by the Central Government on recommendations of the Tariff Commission, is being omitted, as the commission has been wound up.
[Clause 107]
- Schedule I is being amended to reflect the change in tariff rates for a number of items. [Will come into effect as per the dates specified therein]
Amendments to Notifications issued under Customs Tariff Act:
[Clause 104]
- On recommendation of the GST Council, GST Compensation Cess is being exempted on imports in SEZ by SEZ units or authorized developers with effect from 01/07/23.
[Clause 105]
- Notification No. 37/2023-Customs, is being validated from 01/04/23-10/05/23, to provide exemption from basic customs duty and Agriculture Infrastructure and Development Cess(AIDC) on imports of certain goods subject to fulfilment of the requirements.
- Notification No. 31/2024-Customs, pertaining to the India-UAE CEPA is being amended as consequential changes in duty rates on precious metals.
- Notification No. 11/2018-Customs, is being amended, granting exemption to a number of goods from Social Welfare Surcharge (SWS).
- Notification No.11/2021-Customs, is being amended to revise the AIDC rates on specific goods.
- Notification No. 38/2024-Customs is being amended, the duration for export of articles of foreign origin imported to India for repairs has been extended to 1 year.
- Notification No. 39/2024-Customs is being amended, the time period of duty-free re-import of goods exported out India has been increased to 5 years.
- Several other notifications are being amended to allow for granting of exemption in Basic Customs duty, existing exemptions being allowed to lapse, and review of the granted exemptions
Amendments to Notifications issued under Central Excise Act: [Clause 108]
- Notification No 12/2012-Central Excise is being amended, to extend the time period of submission of the final Mega Power Project certificate from 120 month to 156 months.
[Clause 109]
- Notification No 12/2017-Central Excise is being amended, as a result, the Clean Environment Cess, levied and collected as a duty of excise, is being exempted on excisable goods lying in stock as on 30th June, 2017, subject to payment of appropriate GST Compensation Cess on the subsequent supply of such goods.
Amendments under CGST Act:
[Clause 110, 147 and 151]
- Section 9 being amended to exclude un-denatured extra neutral alcohol or rectified spirit used in manufacture of alcoholic liquor for human consumption from the purview of central tax. Similar amendments also proposed in section 5(1) of IGST Act [Clause 147] and section 7(1) of UTGST Act [Clause 151]
[Clause 112, 148 and 153]
- Section 11A being inserted to empower the government, on the GST council's recommendation to regularize non-levy or short levy of central tax resulting from prevalent trade practice. Similar provisions being proposed in section 6A of IGST Act, section 8A of UTGST Act and section 8A of GST (Compensation to States) Act
- Amendments under CGST Act:
[Clause 113]
- Amendment proposed in sub-section (3) of section 13 to provide for time of supply of services taxable under reverse charge (received from unregistered suppliers) shall be earlier of the date of payment or date of issuance of self-invoice by registered recipient [Clause 114] (retrospective effect from 1st July 2017)
- Insertion of sub-section (5) in Section 16 to regularize ITC availed on tax invoices or debit notes pertaining to the FY 2017-18 to 2020-21, provided that the ITC claims were made in Form GSTR-3B by November 30, 2021
- Amendments under CGST Act: [Clause 114] (retrospective effect from 1st July 2017)
- Insertion of sub-section (6) in Section 16 to permit the availment of ITC on tax invoices or debit notes, in Form GSTR-3B for the period starting from the date of registration was cancelled, until the date of revocation, subject to the condition that the return is filed within 30 days from the date of order of revocation.
- This provision is not applicable if such ITC is time-barred under section 16(4) on the date of cancellation of registration
- In cases where tax has been paid or ITC has been reversed earlier, no refund will be admissible
[Clause 115]
- Section 17(5) is being amended, to restrict the availment of ITC on tax paid under section 74 until FY 2023-24 and to withdraw restriction on availment of ITC on tax paid after the detention, seizure and confiscation of goods under section 129 and 130.
[Clause 117]
- A new proviso being inserted in section 30(2), to prescribe conditions and restrictions for revocation of cancellation of registration
[Clause 118]
- Section 31(3)(f) being amended, to prescribe time period for issuance of self-invoice by registered recipient, in case of reverse charge supplies
[Clause 120]
- Section 39(3) being substituted, to mandate electronic furnishing of return for each month by registered person required to deduct tax at source, irrespective of any deduction made in the month.
[Clause 124 and 149]
- Sub-section (3) is being amended and subsection (15) is being inserted in section 54, to restrict refund of unutilized ITC or IGST paid on export (zero-rated supply of goods) that are subjected to export duty Similar insertion proposed in section 16 of IGST Act [Clause 131]
- Sub-section (1A) is being inserted in section 70, to enable an authorized representative, as directed by proper officer, to appear on behalf of the person summoned, tender statement and produce necessary documents
[Clauses 132 and 133]
- Sub-section (12) is being inserted in section 73 and section 74, to restrict their applicability for determination of tax pertaining to period up to FY 2023-24
[Clause 134]
- Section 74A being inserted, for determination of tax demands (involving fraud, wilful-misstatement, suppression of facts or otherwise), applicable from F.Y. 2024-25
- Common time limit to issue SCN within forty-two months from the due date of furnishing of annual return or erroneous refund
- Time limit for passing order within twelve months from the date of issuance of SCN
- Further extension of six months to pass an order could be availed from the Commissioner/ Proper Officer by recording reasons in writing before the expiry of initial 12 months
- In case of fraud, wilful-misstatement, suppression of facts, the penalty would be equivalent to the tax amount. In other case, penalty is restricted to 10% of tax amount
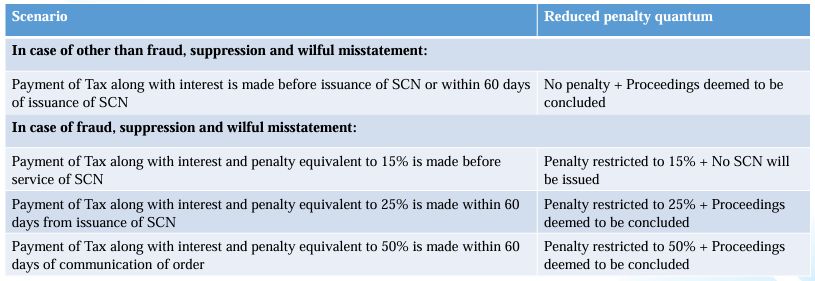
[Clauses 111, 116, 119, 121 to 123, 125 to 130, 136, 137 and 141]
- Sections 10(5), 21, 35(6), 49(8), 50(1), 51(7), 61(3), 62(1), 63, 64(2), 65(7), 66(6), 104(1), 107(11) and 127 being amended, to incorporate reference to section 74A
[Clause 135]
- Sub-section (2A) is being inserted in section 75, to redetermine the penalty in accordance with section 74A(5)(i) (other than fraud cases), in cases where the appellate authority or appellate tribunal has not established charges of fraud, willful misstatement, or suppression of facts against the registered person
[Clause 137]
- Sub-section (6) of section 107 is being amended, to reduce the maximum amount of pre-deposit for filing appeal before Appellate Authority from Rs. 25 crores to Rs. 20 crores under central tax
[Clause 138]
- Section 109 is being amended, to empower Government to notify types of cases that shall be heard only by Principal Bench of Appellate Tribunal. Additionally, the Principal Bench of Appellate Tribunal is further empowered to examine and adjudicate anti-profiteering cases
[Clause 139]
- Sub-sections (1) and (3) of section 112 is being amended, to empower Government to notify date for filing appeal before Appellate Tribunal and provide a revised time limit for filing application before Appellate Tribunal (Effective from 1st August 2024)
- Sub-section (6) of section 112 is being amended, to enable Appellate Tribunal to admit appeals filed by department within three months after expiry of specified time limit of six months
- Sub-section (8) of section 112 is being amended, to reduce the amount of pre-deposit for filing appeals before Appellate Tribunal from 20% to 10% of tax in dispute, and to limit the maximum amount payable as pre-deposit from Rs. 50 crores to Rs. 20 crores in central tax
[Clause 140] (retrospective effect from 1st October 2023)
- Sub-section (1B) of section 122 is being amended, to restrict its applicability to electronic commerce operators, who are required to collect tax at source under section 52
[Clause 142]
- Section 128A is being inserted, to provide for conditional waiver of interest and penalty on demand orders confirmed under section 73 for FY's 2017-18, 2018-19 and 2019-20, subject to the condition that full tax demand is paid before the notified date and registered person withdraws any appeal pending before the Appellate Authority/ Appellate Tribunal or writ petition pending before the Court
- This conditional Waiver does not apply in the case of erroneous refunds
[Clause 143] (retrospective effect from 1st July 2017)
- Sub-section (7) of section 140 is being amended, to extends availment of transitional credit of eligible cenvat credit on account of input services received by an Input Services Distributor prior to appointed day, with respect to invoices received prior to appointed date
[Clause 144]
- Proviso is being inserted in subsection (2) of section 171, to empower Government to notify date from which the Authority under the said section will not accept any application for anti-profiteering cases
[Clause 145]
- Paragraph 8 is being inserted in Schedule III, to provide that activity of apportionment of co-insurance premium by lead insurer to co-insurer(s), where GST has been paid on the entire premium amount by lead insurer, shall not qualify as supply of goods/services
- Paragraph 9 is being inserted in Schedule III, to provide that ceding commission or reinsurance commission shall not qualify as supply of goods/ services, provided that the tax has been paid on gross reinsurance premium
[Clause 146]
- No refund shall be made of all taxes paid or input tax credit reversed, which would not have been so paid, or reversed if section 114 been in force at all material times
[Clause 150]
- Section 20 is being amended, to reduce maximum amount of pre-deposit payable for filing an appeal before appellate authority from Rs. 50 crores to Rs. 40 crores of IGST
- Additionally, it proposes to reduce maximum amount payable as pre-deposit for filing an appeal before appellate tribunal from Rs. 100 crores to Rs. 40 crores of IGST
© 2024, Vaish Associates Advocates,
All rights reserved
Advocates, 1st & 11th Floors, Mohan Dev Building 13, Tolstoy
Marg New Delhi-110001 (India).
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist professional advice should be sought about your specific circumstances. The views expressed in this article are solely of the authors of this article.


