The Republic of Tunisia deposited its Instrument of Accession to
the Geneva Act of the Hague Agreement Concerning the International
Registration of Industrial Designs on 13 March 2012. The Geneva Act
will enter into force in the Republic of Tunisia, on 13 June
2012.
The Hague Agreement is an international registration system for
industrial designs. This agreement provides for the protection of
industrial designs in several countries and organisations by means
of a single international design application, filed with the
International Bureau of the World Intellectual Property
Organization (WIPO) in Geneva, Switzerland. The design application
must designate the countries in which the applicant wishes to
secure design protection. In other words, a single international
design application may be filed designating several countries
instead of having to file separate national applications in each
country.
An international design registration has, in each designated
country, the same effect as if the design had been registered in
the country concerned and is subject to the relevant national law.
The designated countries retain the right to exclude from
protection any designs that do not qualify for protection under
their national laws.
In terms of the Hague Agreement, multiple designs may be included
in a single design application but all products relating to the
design must fall in the same class under the Locarno
classification. Revocation proceedings may be brought against a
registered design on the grounds that it does not qualify for
protection in terms of the national law of any of the designated
countries.
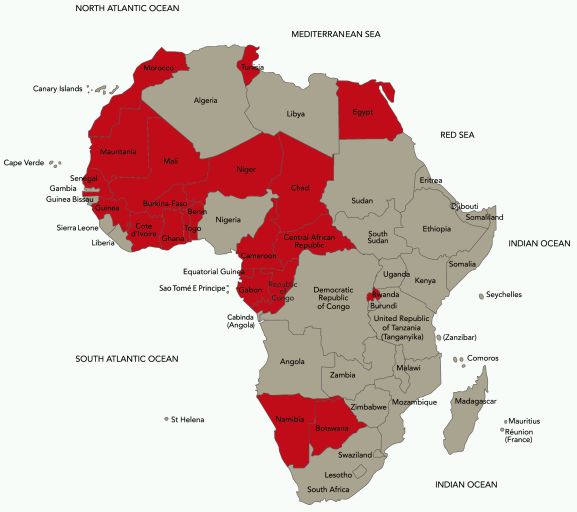
Of the contracting parties to the Hague Agreement, 14 are from
Africa. If one designates all possible African contracting parties
in an international design application, one ends up with a total of
22 African countries covered by the design application.
The African countries and regional organisation that have acceded
to the Hague Agreement include:
Benin (member of OAPI)
Botswana
Egypt
Gabon (member of OAPI)
Ghana
Ivory Coast (member of OAPI)
Mali (member of OAPI)
Morocco
Namibia
Niger (member of OAPI)
Republic of Rwanda
Senegal (member of OAPI)
Republic of Tunisia
OAPI which currently has 16 member countries, namely Benin, Burkina
Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Côte
d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Guinea,
Guinea Bissau, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Senegal and Togo.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.
We operate a free-to-view policy, asking only that you register in order to read all of our content. Please login or register to view the rest of this article.

