In Nigeria, Tax is a very important aspect of our internal revenue generation and as we all know, Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) contribute a huge part of tax generation in Nigeria. Generally, MSMEs are seen as very important and no doubt unquestionable tools in the industrialization process of Nigeria. A small Enterprise is a business with not more than N25 million turnover while a medium enterprise is a business whose turnover is between N25 million to N100 million but not above 100 million naira. Taxation is central to the current economic development agenda in Nigeria, in 2022, the Chairman of the Federal Inland Revenue Service boasted of generating over $22 billion in taxes. It plays a vital role in the overall economic stabilization and management in Nigeria. The following are the taxes required by MSMEs to comply with;
1. COMPANY INCOME TAX (CIT):
- The Tax is charged on the profits from all sources generated by companies operating in Nigeria.
- It is charged on both resident and nonresident companies making profits in Nigeria on their Nigeria-source income.
- The percentage rate of the tax is 30% of the total profit of a company. This rate, however, applies to only companies with N100million and above in turnover.
- Companies with N25 million turnover but not more than N100 million turnover pay 20% of their total profits as CIT.
- For small businesses with less than N25 million turnover, they are exempt from paying Company Income Tax.
- The implementation of Company Income Tax is governed by the Companies Income Tax Act (CITA) Cap C21, LFN 2004 (as amended).
- CIT returns for existing companies are to be filed within 6 months after the accounting year.
- CIT returns for newly incorporated companies are to be filed within 18 months from the date of incorporation or not later than 6 months after the end of its accounting year.
- Shipping and Airline transport companies are now mandated to present to their regulatory agencies, evidence of income tax filings for the preceding year, and Tax Clearance Certificate for three (3) preceding tax years in order to obtain their compliance licenses and permits in order to carry on business in Nigeria.
- Companies engaged in shipping and Air transport business, where they fail to provide a separate financial statement for their Nigeria operations, are now required to submit a certified copy of its detailed gross revenue statement covering their Nigeria operations and showing the full amount earned over the relevant period.
- The rural investment allowance of 10% on qualifying expenditure incurred on plant and equipment has been repealed. Taxpayers can no longer claim additional investment allowance of 10%. This, however, does not affect qualifying assets acquired on or before 28 May 2023.
- Tax exemption of incomes in convertible currencies is no longer applicable and has been repealed by the New Finance Act 2023. However, this does not affect a company that has set aside reserved funds until their reserved funds are fully utilized or until the five (5) year limit effluxes whichever occurs first.
2. VALUE-ADDED TAX (VAT):
- Governed by Value Added Tax Act Cap V1, LFN 2004 (as amended) is known as a consumption tax.
- VAT is tax paid when goods are purchased, and services rendered.
- The VAT tax rate in Nigeria is 7.5% (increased from 5% on 1st February 2020) on goods and services.
- It is a multi-stage tax, but it is usually borne by the final consumer.
- This tax is charged on goods and services produced within or imported into the country except those specifically exempted by the Value Added Tax Act. Goods such as Medical and Pharmaceutical products, Basic food items, Books and Educational materials, baby products, locally produced fertilizer, agricultural and veterinary medicine, farming machinery and farming transportation equipment, plants, and machinery for use in export processing zones or free trade zones are not taxable under VAT.
- VAT returns are to be filed on the 21st day of the month following the month of the transaction.
- Also, zero-rated items which include non-oil exports, goods and services purchased by diplomats, and goods and services purchased by humanitarian donor-funded projects are exempted from tax.
- Note that companies with less than N25 million turnover are exempted from paying VAT.
- Examples of VATable services includes services rendered by lawyers, traders, engineers, accountants, contractors, consultants, entertainers, caterers, Realtors, and landlords, and so on.
- The timeline for VAT remittance by persons so appointed by the FIRS has been brought forward to the 14th of the following month from the previous 21st date.
- Taxable goods purchased via electronic and digital platforms operated by a nonresident supplier appointed by the FIRS for the collection of tax and imported into Nigeria shall not be subjected to further tax before clearing by the Nigerian Customs Service provided that at the point of clearing the goods, the importer shall provide proof of appointment and registration and such other document as may be required by FIRS.
- The Finance Act amended the term 'building' to include the land only and excludes fixtures and structures easily removable from the land. The implication of this is that statutory VAT exemption on buildings will not extend to fixtures and structures outside the new definition of a building.
3. CAPITAL GAINS TAX (CGT):
- It is governed by Capital Gains Tax Act, Cap C1 LFN 2004 (as amended).
- CGT is a flat rate tax, taxed at the rate of 10% of chargeable gains.
- This tax is imposed on the income of individuals, corporate sole, or body of individuals resident in Nigeria by the State Internal Revenue Service.
- It is also administered on nonresidents, members of the Armed forces, police, and officers of the Nigerian Foreign Service by the Federal Inland Revenue Service (FIRS).
- P.A.Y.E is to be remitted to the appropriate commission on/before the 10th date of every month following the month of deduction.
- Except specifically exempted by the Act, all chargeable assets (all forms of property whether or not situate in Nigeria) are subject to CGT when disposed at a gain.
- Gains arising from the disposal of decorations awarded for valor and gallant conduct, life insurance policy, Nigerian government securities, stocks, and shares are all exempted from CGT.
- Note that, the disposal of shares in a Nigerian company worth N100 million or above is subjected to CGT unless the proceeds are re-invested within 12 consecutive months in the shares of a Nigerian company.
- CGT will also apply for compensation for the loss of office where the compensation exceeds N10 million. " Capital Gain Tax returns are to be filed twice a year, on the 30TH of June and the 31st of December.
- Under the new Finance Act 2023, digital assets are now considered taxable assets under Capital Gains Tax. Note, that the term digital assets were not defined to determine assets that expressly fall under it. Generally, digital assets include (but are not limited to) convertible virtual currency and cryptocurrency, stablecoins, and non-Fungible tokens (NFTs). However, there still remains uncertainty as to the operation of this new taxation law, this is because while the CBN banned the operation of cryptocurrency which is a digital asset, the Finance Act recognizes it as operational.
- The new Finance Act 2023 introduces a new provision for the deduction of losses accrued in the disposal of chargeable assets from the gains accruing to the person disposing of that asset. However, the loss shall only be deductible against the same type of asset.
- Shares and stocks now qualify under the class of assets entitled to a rollover relief provided that for the rollover relief to be enjoyed according to sections 30 and 31 of the Capital Gains Tax Act, the proceeds from qualifying disposals must be reinvested in the acquisition of eligible shares in the same or other Nigerian companies, within the same year of assessment.
4. Personal Income Tax (PIT):
- Personal Income Tax is guided by the Personal Income Tax Act Cap P8 LFN 2004 (as amended). " PIT is charged based on how you earn, hence, the need for the acronym P.A.Y.E which means Pay As You Earn.
- This tax is imposed on the income of individuals, corporate sole, or body of individuals resident in Nigeria by the State Internal Revenue Service.
- It is also administered on non-residents, members of the Armed forces, police, and officers of the Nigerian Foreign Service by the Federal Inland Revenue Service (FIRS).
- P.A.Y.E is to be remitted to the appropriate commission on/before the 10th date of every month following the month of deduction.
- PIT returns are to be filed on/ before the 31st of March of every year.
- The tax rates applied on taxable income are as follows.
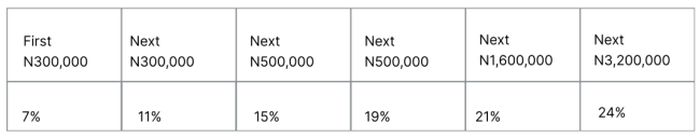
- Note that the minimum tax rate is 1% of total income and is applicable where the taxable income is below N300,000.
- Also, individuals who earn the gross income of National Minimum Wage (N30,000) or below N30,000 are exempted from paying PIT. " Let's take for example, Mr. A lives in Masaka Nasarawa State but works in Wuse zone 3 F.C.T, since Personal Income Tax is payable to the State government, Mr. A will remit his tax to the State Internal Revenue Service, F.C.T
- The new Act re-introduced the tax reliefs on amounts paid as premiums on deferred annuity and personal and spouse's insurance. There is now a tax allowance for the deduction of personal or spouse life insurance premiums or contractual deferred annuity. Note that, this relief shall not apply where any portion of a deferred annuity is withdrawn before the end of five (5) years from the date the premium was paid.
To view the full article, click here.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

