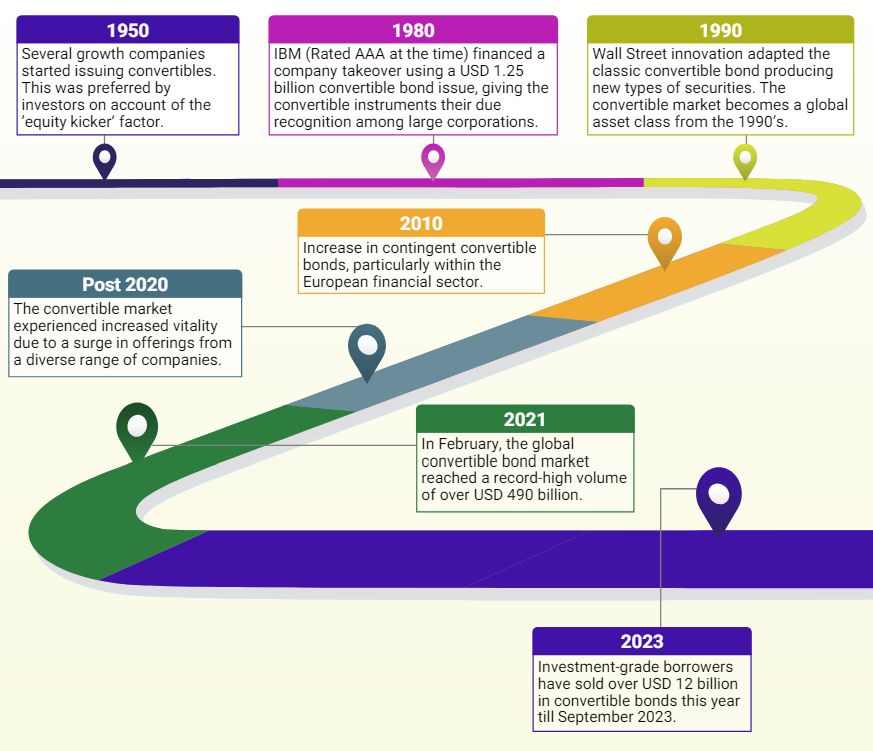
Convertible securities emerged during the nineteenth century in the U.S. This was during a period in which securing capital in a swiftly expanding nation posed several difficulties, which led to the incorporation of convertible clauses in mortgage bonds. This addition aimed to attract investors primarily for funding the railroad construction. Subsequently, several companies across various industries began adopting such financial instruments.
Owing to the increasing relevance of convertible debt instruments, it is crucial to understand the methods used to value convertible debt.
History of Convertible Debt Instruments
Types of Convertible Debt Instruments
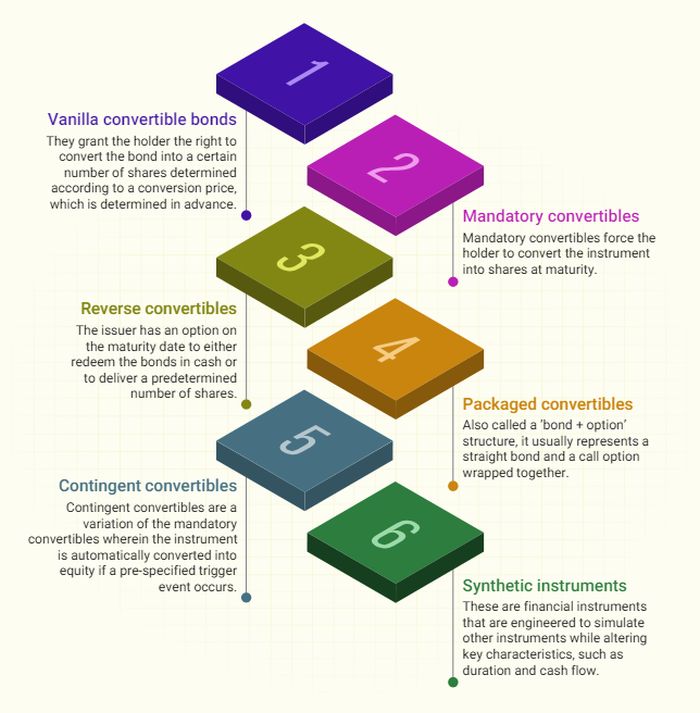
What are optionally convertible debt instruments?
In its simplest form, optionally convertible debt instruments are hybrid instruments that give the investor the option to:
- Hold the instrument to maturity and redeem it for par value or
- Exercise the conversion option and receive shares.
These are hybrid securities that have both debt-like and equity-like features. The arrangement can be equated to subscribing to the debt and buying a call option on the company's equity.

Complex convertible debt instruments can have features such as periodic call (redeemable) and/or put (retractable) features, or floating coupon rates, or are exchangeable into other exotic securities, or the underlying has an irregular dividend structure.
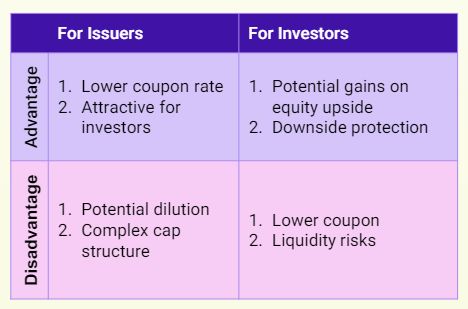
What are the advantages and disadvantages of optionally convertible debt instruments?
Valuation methods used to value optionally convertible debt instruments
The valuation of optionally convertible debt instruments varies from the valuation of a straight bond primarily due to the different pay-off structures based on the terms of the instrument.
The value of a convertible bond is the sum of two main components, namely, the value of the optionfree bond and the value of the options on the underlying instrument (generally common stock). The bond component is influenced by three main parameters, which are maturity, coupon rate, and yield to maturity (discount rate).
There are a variety of ways to model convertible instruments, including closed-form and numerical solutions.
- Closed-form solutions such as the Black Scholes Merton Model can only be used with a restricted set of assumptions. Therefore, numerical solutions are frequently used in practice.
- Numerical solutions such as lattice methods, finite difference methods, or Monte Carlo Simulations can include a path-dependent pay-off structure, allowing a more realistic implementation of convertible bond features.
In this article, we will discuss three widely used methods for valuing optionally convertible debt instruments:

To view the full article, click here.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.
We operate a free-to-view policy, asking only that you register in order to read all of our content. Please login or register to view the rest of this article.

