The semiconductor industry is a cornerstone of innovation and economic power in the global high-tech arena. Recognising its strategic importance, China has embarked on an ambitious journey to transform its semiconductor landscape and achieve self-sufficiency.
The current state of play
China is the world's largest consumer of semiconductors, accounting for over half of the global chip sales. Despite this, the nation has historically relied heavily on imports to meet its demands. In 2020, imports constituted a staggering 83% of total chip sales within the country. This dependency has catalysed change, prompting China to invest heavily in its domestic semiconductor industry.
Strategic investments and initiatives
China's semiconductor industry has seen significant strategic investments and initiatives to bolster its position in the global market. The country has focused on advancing node manufacturing, with companies like Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation (SMIC) making notable progress in producing smaller, more efficient semiconductor components.
In the first quarter of 2024, SMIC shipped 1.7 million wafers, achieving the second-highest revenue in its history for the same period at CNY 12.594 billion, a year-over-year increase of 19.7%, and climbing to the position of the world's second-largest pure-play foundry in the current period, behind only TSMC.
Additionally, China has targeted the memory market to reduce dependency on foreign suppliers, with key players like Yangtze Memory Technologies Co. (YMTC) leading the charge. The industry is also heavily investing in Silicon Carbide (SiC) technology, which is crucial for high-performance 5G and AI applications.
Furthermore, China is enhancing its capabilities in advanced packaging, with companies like JCET providing innovative solutions for emerging technologies. Despite facing challenges from international sanctions, China continues to invest in cutting-edge manufacturing equipment to strengthen its semiconductor supply chain. These efforts collectively aim to secure China's technological independence and global competitiveness in the semiconductor sector.
Advancements and challenges in China's semiconductor equipment industry
According to TrendForce's analysis of industry data and financial reports from major companies, China's domestic equipment industry can handle various stages of semiconductor manufacturing processes (excluding lithography machines). Locally produced equipment in China has achieved high localisation rates in processes like photoresist stripping, cleaning and etching. Recent progress has also been made in CMP, thermal processing and deposition. However, challenges remain for Chinese equipment manufacturers in measurement, coating, development, lithography and ion implantation.
| Localisation rate | Chinese representative | |
| Photoresist stripping equipment | Above 90% | BEST (Mattson Technology Inc.) |
| Cleaning equipment | Around 20% | NAURA, ACM Research |
| Etching equipment | Around 20% | NAURA, Cmesemicon, BEST |
| Heat treatment equipment | Around 20% | NAURA, BEST |
| PVD equipment | Around 10% | NAURA |
| CMP equipment | Around 10% | HWATSING TECHNOLOGY |
| Coating and developing equipment | Breakthrough | KINGSEMI |
| Photolithography equipment | Breakthrough | SMEE |
Foundry outlook
Based on IC Wise's analysis, the chip industry in mainland China is expected to turn from a cyclical trough to growth in 2024, increasing by 12%. The overall recovery of the foundry market demand in mainland China is expected to be positive in 2024, with an increase of 9%. Semiconductor equipment in mainland China is expected to grow in 2024, with a rise of 9.6%.
In 2023, mainland China and the global chip industry entered the trough of the industry cycle. The primary revenue from mainland China chip design companies' foundry industry (excluding China Resources, Silan and other IDM) inevitably followed the decline. China foundry industry revenue declined by 21% to USD11.4 billion.
In 2024, only the PC market is less optimistic due to new energy vehicles, wind energy storage to maintain growth and mobile phones and consumer electronics to return to positive growth. Demand for mainland China's chip design industry will usher in a wave of new growth cycles, improving the capacity utilisation rate of the Chinese mainland foundry. CoreMou Research expects the mainland China foundry market to grow 9% to USD 12.4 billion in 2024. Among them, the capacity utilisation rate of eight-inch fabs will increase to 90%, and the capacity utilisation rate of 12-inch fabs will increase to 78%.
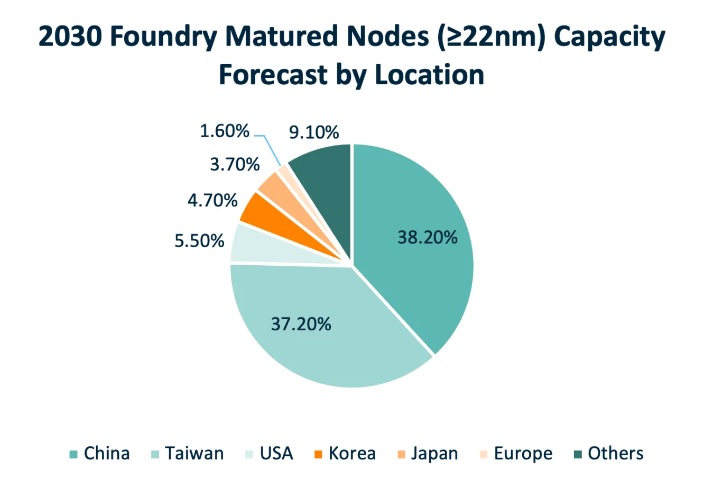
Source: idc.com
IDC predicts that by 2030, China's mature semiconductor process market (= 22nm) will grow significantly, reaching nearly 40% market share (up from 30% in 2023) through government policies and subsidies, coupled with the support of China's enormous domestic demand market. China's influence on the global semiconductor production capacity will also increase as it pressures International Device Manufacturers (IDMs) and foundries specialising in mature nodes.
Equipment industry outlook
The semiconductor equipment market in mainland China reached a record USD 34.2 billion in 2023, an increase of 8%, with a global share of 30.3%; it is expected to reach USD 37.5 billion in 2024, an increase of 9.6%.
In 2023, the overall revenue of domestic semiconductor equipment companies grew by more than 17.6% to USD 4 billion, and the localisation rate of equipment reached 11.7%. IC Wise predicted that in 2024, mainland China's equipment manufacturers' revenue will grow to USD 5.1 billion, and the localisation rate will reach 13.6%. Under the general trend of China's domestic substitution, domestic equipment manufacturers will accelerate their expansion, and the equipment industry will enter a new stage of comprehensive and rapid development.
NAURA, ACM Research, VITAL, JSJD and other equipment companies have grown significantly, showing a platform development trend. AMEC, HWATSING TECHNOLOGY, Shanghai Kingstone and other top enterprises focusing on etching, CMP and ion implantation equipment have grown significantly in revenue.
Export controls impact
The journey is not without its challenges. From an export controls perspective, the US has continued to impose export control restrictions on Chinese firms, targeting advanced semiconductors and semiconductor manufacturing equipment (SME). The goal is to prevent Chinese firms from moving into nonplanar technology processes like FinFET and Gate All Around Field Effect Transistors (GAAFET). Chinese firms are now closely tied to the speed of developing domestic toolmaking and manufacturing capabilities. Although US controls impact cutting-edge capabilities, Chinese firms continue to expand capacity at mature nodes where domestic demand remains high.
The road ahead for China's semiconductor industry
China's semiconductor industry is at a crossroads, facing both opportunities and obstacles. The nation's commitment to reducing reliance on foreign technology is clear, but the path to self-sufficiency is complex and fraught with geopolitical tensions.
As China continues to navigate these waters, the world watches closely. The outcome of China's semiconductor quest will shape the future of its own technological landscape and have far-reaching implications for the global semiconductor industry.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

